Irradiance on a tilted surface that is reflected off the ground, $$E_g$$ , is calculated as a function of the irradiance on the ground, usually assumed to be $$GHI$$, the reflectivity of the ground surface, known as albedo, and the tilt angle of the surface, $$\theta_{T},{surf}$$ :
$$E_{g}=GHI\times albedo\times\frac{\left(1-\cos\left(\theta_{T},{surf}\right)\right)}{2}$$
The model for ground reflected irradiance $$E_g$$ develops from the following assumptions:
- The array is infinitely long.
- Irradiance on the ground is uniform and equal to $$GHI$$, i.e., horizon blocking and near-field shading by the array is ignored.
- Irradiance reflects from the ground equally in all directions, i.e., the ground is a diffuse or Lambertian reflector.
- The ground is visible to the array from the point of intersection of the array’s slope projected to the ground, to the infinite horizon.
With these assumptions the model for $$E_g$$ can be derived using a view or configuration factor. The view factor quantifies the fraction of diffuse reflected irradiance from one surface $$A_1$$ that impinges on a second surface $$A_2$$. In the equation above for $$E_g$$, the term $$\frac{1-cos{\theta_{T,surf}}}{2}=F_{A_1\rightarrow A_2}$$ is the view factor from surface $$A_1$$, the ground, to surface $$A_2$$, the module.
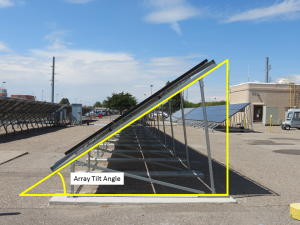
To derive this model, consider an infinite strip $$dA_1$$ on the ground of differential width $$dx$$ that is parallel to the array. Denote the array’s face as $$A_2$$, and the view factor from $$dA_1$$ to $$A_2$$ as $$F_{dA_{1}\rightarrow A_2}$$. The irradiance per unit length (W / m) reflecting from the strip $$dA_1$$ is $$GHI\times albedo\times dx$$. The contribution to irradiance per unit length (W / m) on $$A_2$$ from reflected irradiance from $$dA_1$$ is
$$dE_{g}=GHI\times albedo\times F_{dA_{1}\rightarrow A_{2}}\times dx$$
Let $$x$$ be a coordinate axis on the ground with origin under the lower, forward edge of the array, parallel to the rear-facing normal vector to the array, with negative direction toward the horizon behind the array. Consider $$A_1$$ to be the half-plane on the ground defined by $$x\leq x_0$$, and $$A_2$$ to be the rear-facing side of an infinitely long strip of width $$L$$ above the half plane with edges parallel to the ground. The total irradiance on $$A_2$$ per unit area (W/m2) from irradiance reflected from $$A_1$$ is
$$\begin{align}E_g & = \frac{1}{A_2}\int dE_g =\frac{1}{L_2}\int{-\infty}^{x_0}GHI \times albedo\times F_{dA_1\rightarrow A_2}dx \\ & =GHI \times albedo \times \int_{-\infty}^{x_0}\frac{F_{dA_1\rightarrow A_2}}{L_2}dx \\ & = GHI \times albedo \times F_{A_1\rightarrow A_2} \end{align}$$
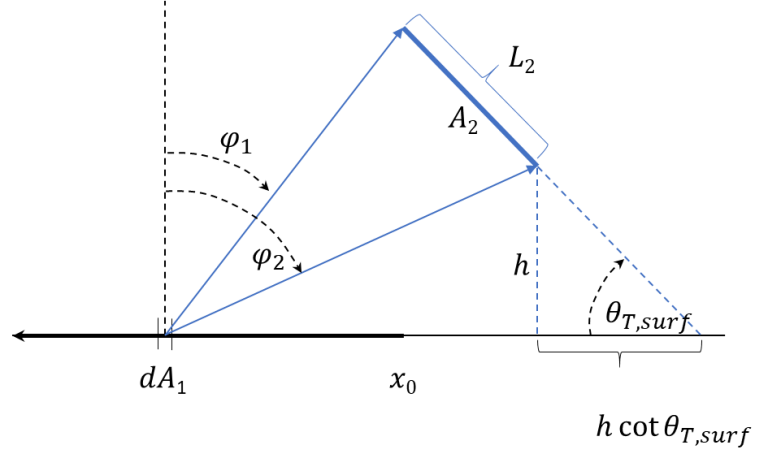
The view factor $$F_{dx \rightarrow A_2}$$ is given by the formula
$$F_{dA_{1} \rightarrow A_2} = \frac{1}{2} \left( \sin \left( \phi_2 \right) – \sin \left( \phi_1 \right) \right) $$
Rewriting the terms in the equation for $$F_{dA_{1} \rightarrow A_2}$$ as
$$\sin \phi_2 = \cos \left(90 – \phi_2 \right) = \frac {x-h \cot \theta_{T,surf}}{\sqrt{\left(x – h \cot \theta_{T,surf} \right) ^2 + h^2}}$$
$$\sin \phi_1 = \cos \left(90 – \phi_1 \right) = \frac{x – h \cot \theta_{T,surf} – L_2 \cos \theta_{T,surf}}{\sqrt{\left(x – h \cot \theta_{T,surf} – L_2 \cos \theta_{T,surf} \right)^2 +\left(L_2 \sin \theta_{T,surf} + h \right)^2}}$$
Substituting and evaluating the integral $$F_{A_1 \rightarrow A_2} = \int_{-\infty}^{x_0}\frac{F_{dA_1\rightarrow A_2}}{L_2} dx$$ obtains
$$F_{A_{1} \rightarrow A_{2}} = \frac{1}{2} \left[L_{2} \cos \theta_{T,surf} – \sqrt {\left(x_0 – h \cot \theta_{T,surf} \right)^2 + h^2} + \sqrt{ \left(x_{0} – h \cot \theta_{T,surf} – L_{2} \cos \theta_{T,surf} \right)^2 + \left(L_{2} \sin \theta_{T,surf}+ h \right)^2} \right] $$
When the full half plane is visible to the rear facing side of the array, $$x_{0} = h\cot \theta_{T,surf}$$ which reduces the above expression to
$$F_{A_1 \rightarrow A_2} = \frac{1}{2} \left(1 + \cos \theta_{L,surf} \right)$$
When $$A_2$$ is taken to be the front-facing surface and $$A_1$$ is the half-plane $$x\geq h \cot \theta_{T,surf}$$, the view factor $$F_{A_{1}\rightarrow A_{2}}$$ is calculated in a similar manner to obtain
$$F_{A_{1}\rightarrow A_{2}} = \frac{1}{2}\left( 1 -\cos \theta_{T,surf} \right)$$