Inverter efficiency is the ratio of the usable AC output power to the sum of the DC input power and any AC input power. Typical grid-tied inverter efficiencies exceed 95% under most operating conditions Efficiency changes as a function of AC output power, DC voltage, and sometimes inverter temperature. Sandia National Laboratories and BEW have worked together to develop a test protocol to measure inverter efficiency as a function of AC output power and DC voltage. This protocol has been adopted by the California Energy Commission (CEC) and any inverter used in a CEC approved PV system must be tested by an independent lab to this protocol. The CEC lists test results for thousands of inverters on its webpage.
An example of a CEC test result is illustrated in the following figure.
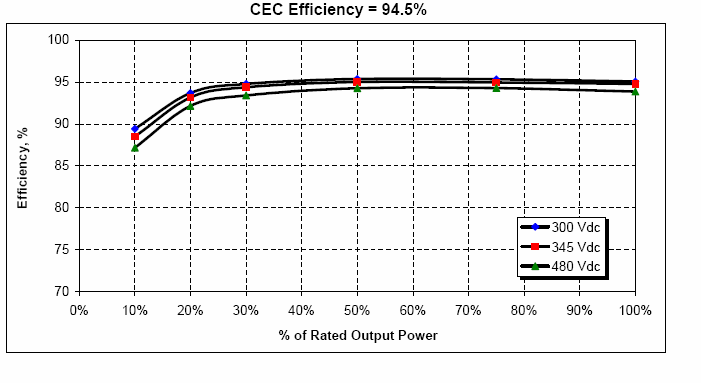
The inverter efficiency is measured at six power levels (10%, 20%, 30%, 50%, 75%, and 100% of rated output AC power) and at three DC voltage levels (Vmin, Vnom, and Vmax) for a total of 18 measurements.
For the purpose of rating and comparing inverter efficiencies, the protocol suggests a weighted average efficiency, which is calculated as a weighted sum of these 18 values. The weighting factors are listed in the table below by AC power level. The weights do not change as a function of DC voltage.
| Inverter AC Power Level | Weighting Factor |
| 10% | 0.04 |
| 20% | 0.05 |
| 30% | 0.12 |
| 50% | 0.21 |
| 75% | 0.53 |
| 100% | 0.05 |